文章目录
- fragment组件
- teleport组件
- Suspence组件
fragment组件
在Vue2中:组件必须有一个根标签
在Vue3中:组件可以没有根标签,内部会将多个标签包含在一个 Fragment 虚拟元素中
好处:减少标签层级,减小内存占用
teleport组件
Teleport 是一种能够将我们的组件 html 结构移动到指定位置的技术
<teleport to="移动位置">
<div v-if="isShow" class="mask">
<div class="dialog">
<h3>我是一个弹窗</h3>
<button @click="isShow = false">关闭弹窗</button>
</div>
</div>
</teleport>我们先做这样一个效果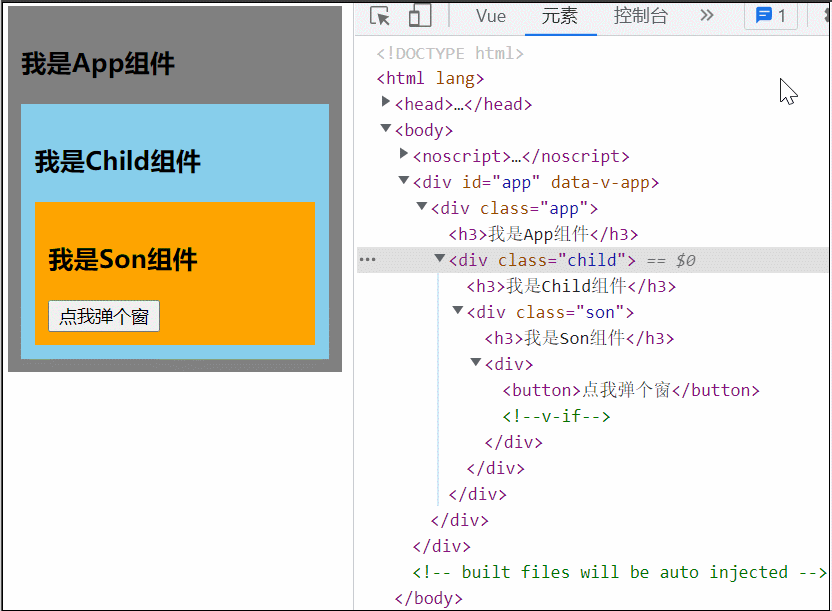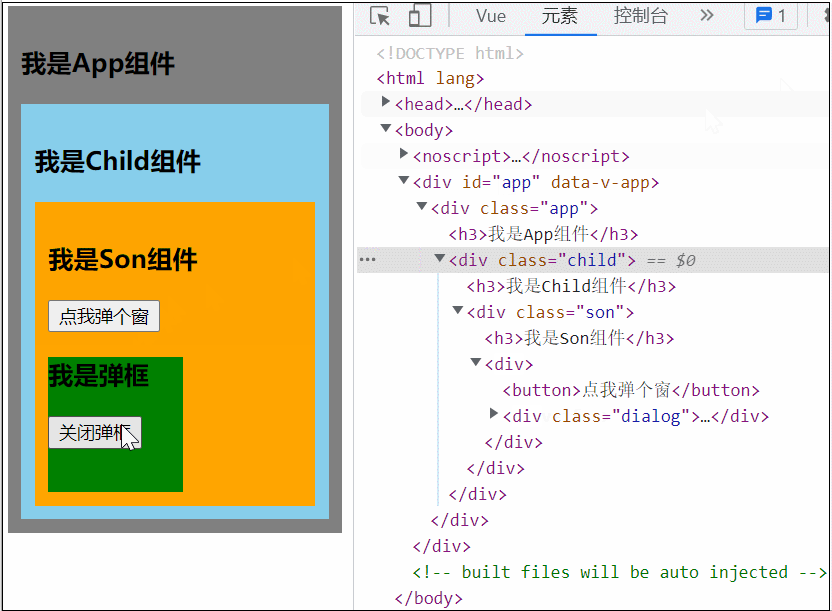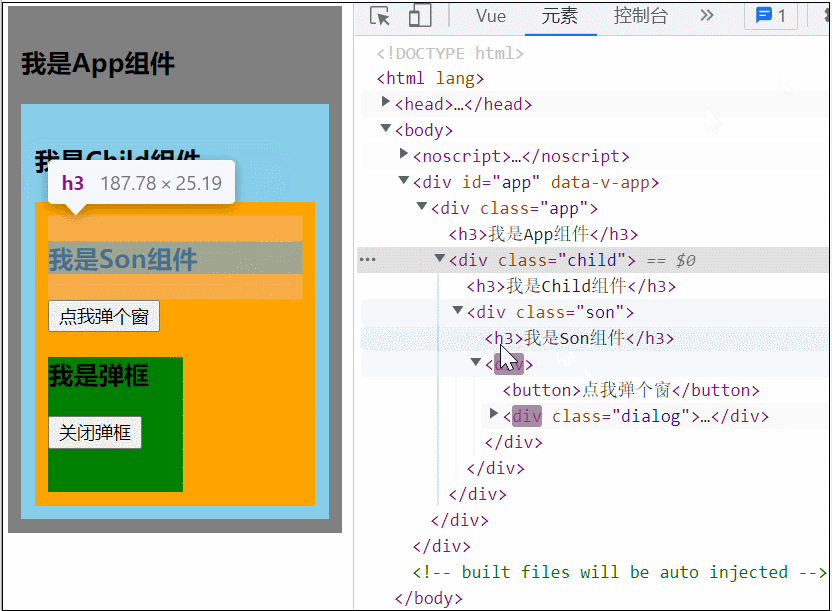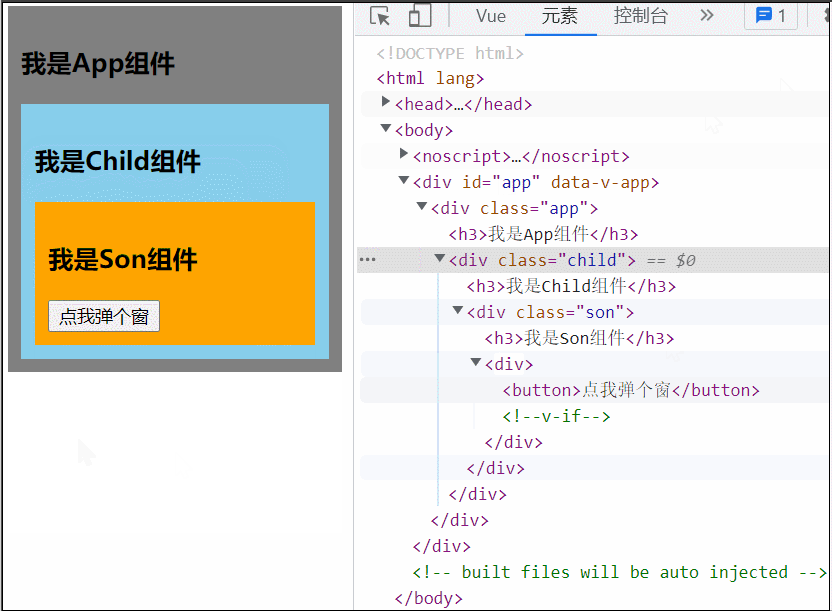
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<Child/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "@/components/Child";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {Child}
}
</script>
<style>
.app {
background-color: gray;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>Child.vue
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>我是Child组件</h3>
<Son/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from "@/components/Son";
export default {
name: 'Child',
components: {
Son
}
}
</script>
<style>
.child {
background-color: skyblue;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son">
<h3>我是Son组件</h3>
<Dialog/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Dialog from "@/components/Dialog";
export default {
name: 'Son',
components: {
Dialog
}
}
</script>
<style>
.son {
background-color: orange;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>Dialog.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = true">点我弹个窗</button>
<div class="dialog" v-if="isShow">
<h3>我是弹框</h3>
<button @click="isShow = false">关闭弹框</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Dialog',
setup() {
let isShow = ref(false)
return {isShow}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.dialog {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
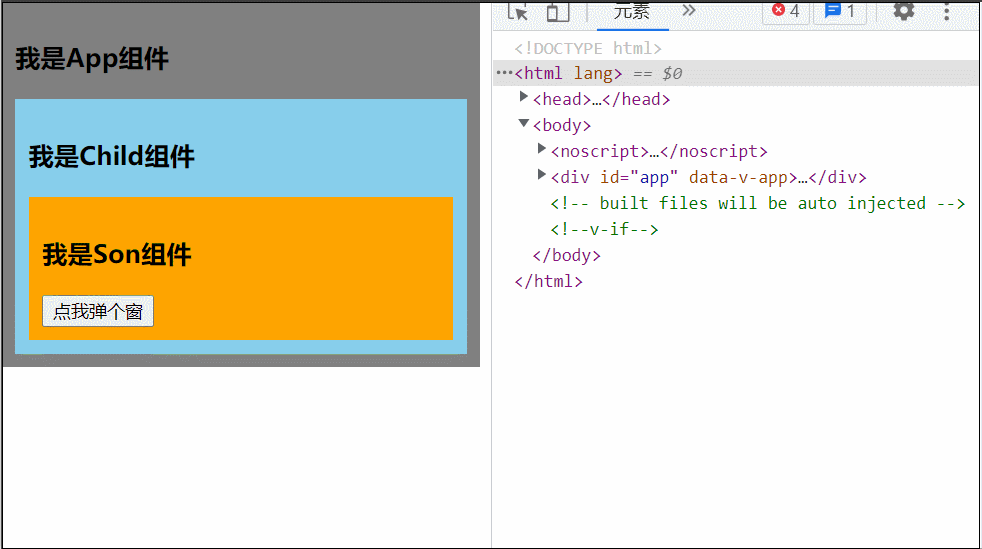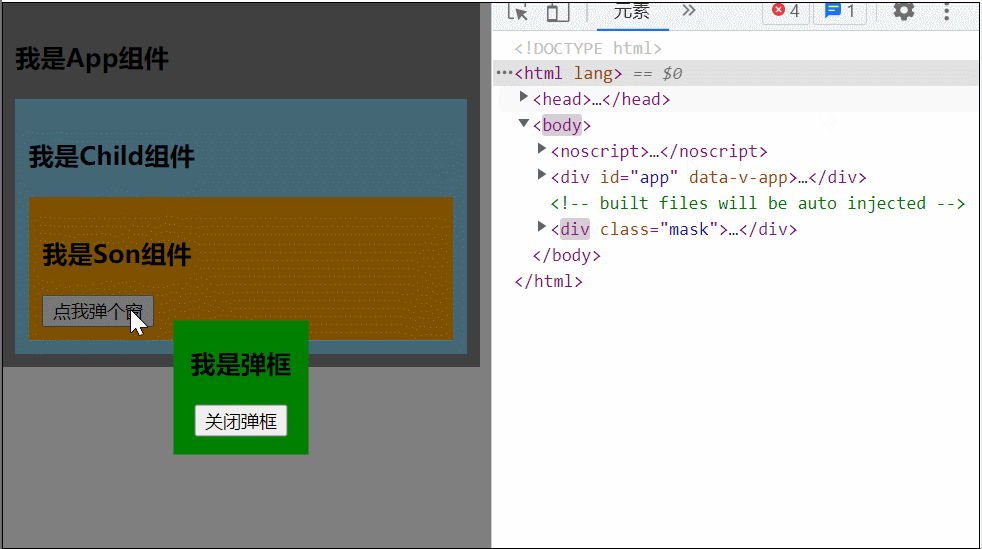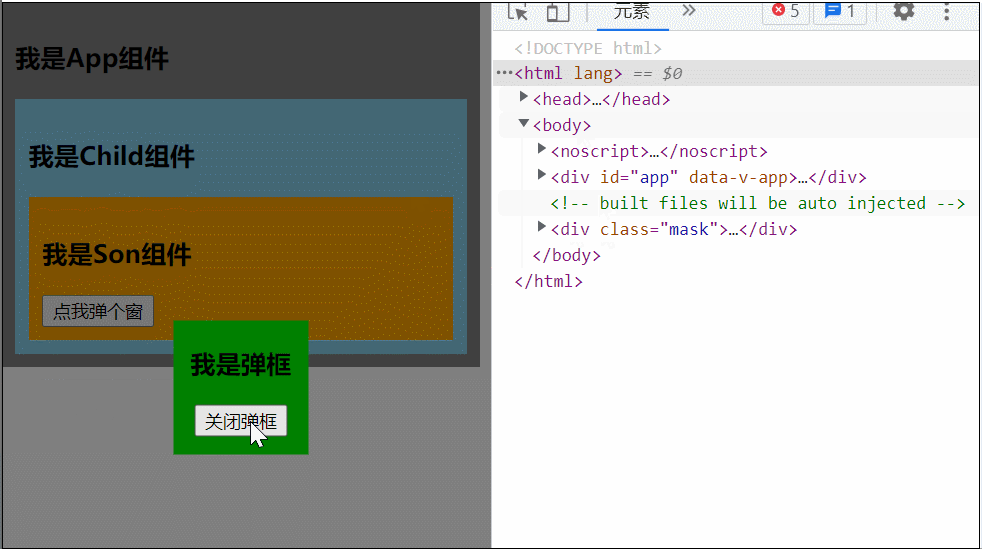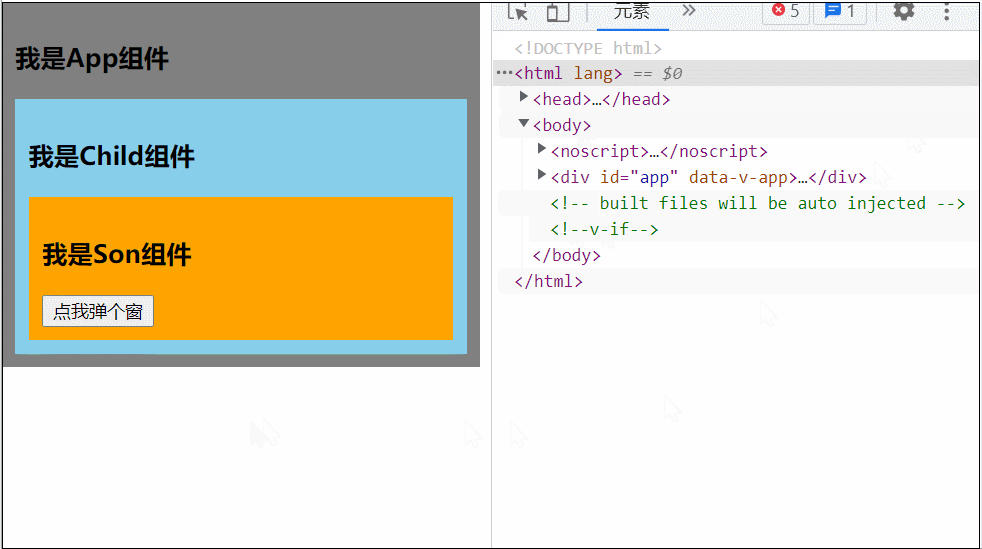
</style>可以看到当 Son 中的 Dialog 展开时,所有父组件都被撑开了,我们可以用 teleport 将弹框移动到 body 里,展示到屏幕中间
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = true">点我弹个窗</button>
<teleport to="body">
<div class="mask" v-if="isShow">
<div class="dialog" v-if="isShow">
<h3>我是弹框</h3>
<button @click="isShow = false">关闭弹框</button>
</div>
</div>
</teleport>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Dialog',
setup() {
let isShow = ref(false)
return {isShow}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.dialog {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
text-align: center;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
.mask {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: rgb(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
</style>Suspence组件
等待异步组件时渲染一些额外内容,让应用有更好的用户体验
使用步骤:
1、异步引入组件
import {defineAsyncComponent} from "vue";//动态引入
const Child = defineAsyncComponent(()=>import('./components/Child'))2、使用Suspense包裹组件,并配置好default与fallback
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<suspense>
<template #default>
<Child/>
</template>
<template #fallback>
<h3>加载中......</h3>
</template>
</suspense>
</div>
</template>首先演示下异步插件。App 内异步引入 Child 组件
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<Child/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//静态引入
//import Child from "@/components/Child";
import {defineAsyncComponent} from "vue";//动态引入
const Child = defineAsyncComponent(()=>import('./components/Child'))
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {Child}
}
</script>
<style>
.app {
background-color: gray;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>为了清楚的看到效果,我们把网络调成高速3G,然后刷新页面,可以很清楚的看到 App组件先展示出来,然后 Child 组件才展示
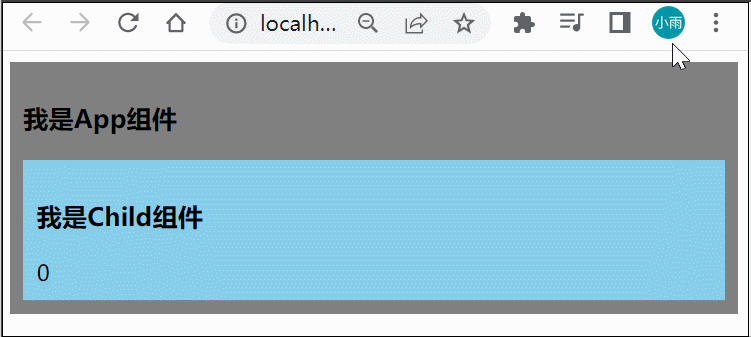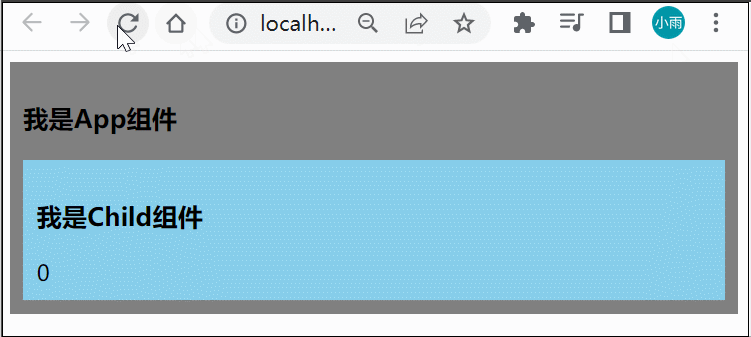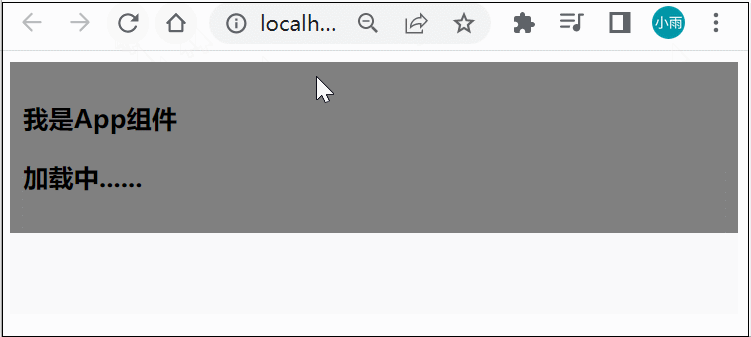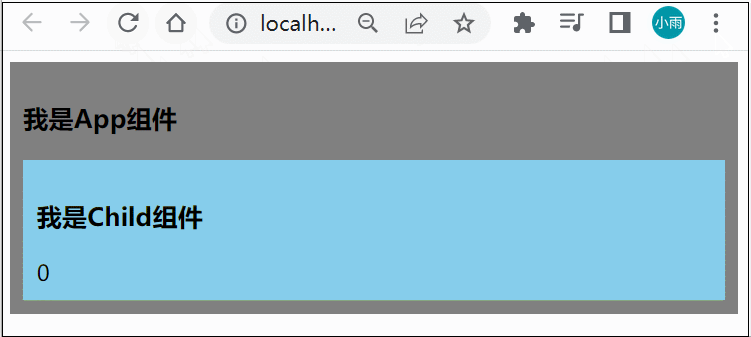
这样体验不是太好,我们可以使用 suspence 来解决这个问题,Suspense 是 Vue3 推出的一个内置的特殊组件,有两个 template slot,刚开始会渲染一个 fallback 内容,直到达到某个条件以后才会渲染正式的内容
修改 App.vue 中代码:
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<suspense>
<template #default>
<Child/>
</template>
<template #fallback>
<h3>加载中......</h3>
</template>
</suspense>
</div>
</template>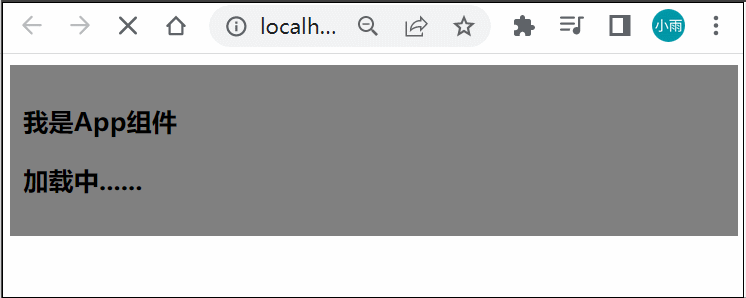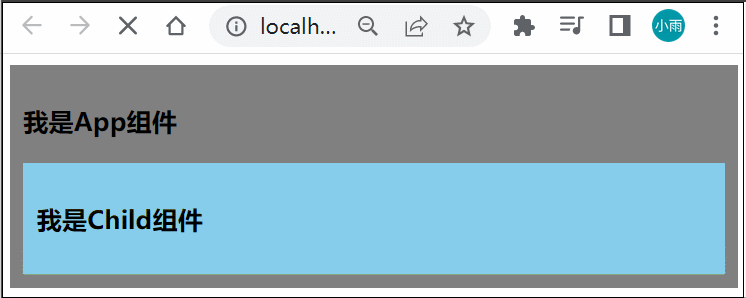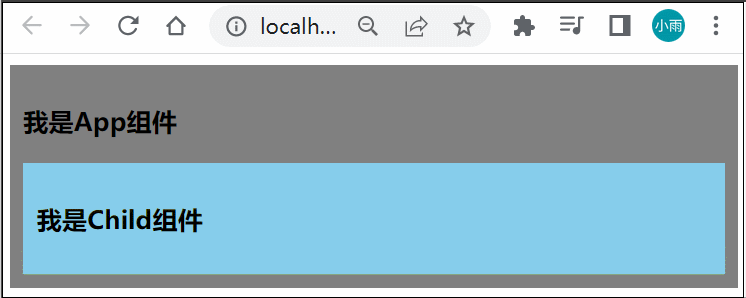
刚才除了把网速调慢可以让 Child 晚一点加载出来,或者修改 Child.vue
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>我是Child组件</h3>
{{ sum }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref} from "vue"
export default {
name: 'Child',
async setup() {
let sum = ref(0)
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({sum})
}, 2000)
})
return await p;
}
}
</script>
<style>
.child {
background-color: skyblue;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>