Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
- The "linked list" should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The "linked list" should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
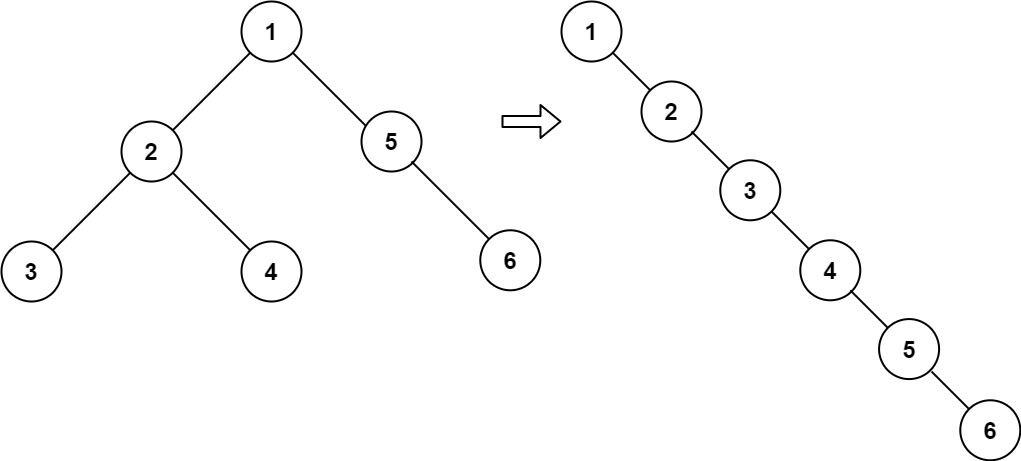
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
这题还进一步问到能否做到空间复杂度是O(1)。在之前114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List用了递归解法,但是空间复杂度是O(n)。要到达O(1)肯定要用迭代法,然而我们常用的的前序遍历迭代法要用到堆栈,空间复杂度还是达到O(n)。因此要另想办法。
首先再来分析一下题目,在114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List 提到的是把根节点的左子树通过递归调用转换成链表后挂到根节点的右子节点上,最终所有节点的左子节点都为空。那为了不用多余的存储空间有没有办法不转换成链表直接把整棵左子树挂到根节点的右侧去呢?答案是肯定的,根据前序遍历的顺序,在左子树没转成链表之前我们就可以知道链表的头节点,就是根节点的直系左子节点,因此可以把左子节点挂到根节点的右侧成为新的右子节点,然后左子节点指向空,而根节点原来的右子树则可以挂到原来左子树的最右侧的那个节点的右侧(这刚好前序遍历的顺序,先左子树再右子树),依次向右处理每个节点(当前节点处理完就没有左子节点只有右子节点),对于存在的左子树的节点都做相同的处理,最终就会得到一个前序遍历顺序的链表。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def flatten(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
"""
if not root:
return None
node = root
while node:
if node.left:
cur = node.left
while cur.right:
cur = cur.right
cur.right = node.right
node.right = node.left
node.left = None
node = node.right








