冒泡排序

public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {
9, 5, 7, 12, 1, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
bubble(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void bubble(int[] a) {
int j = a.length - 1;
do {
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i + 1];
a[i + 1] = temp;
x = i;
}
}
j = x;
} while (j != 0);
}
}
选择排序
public class SelectionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = {
9, 5, 7, 12, 1, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
selection(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void selection(int[] a) {
// 1.选择轮数,a.length - 1
// 2.交换的索引位置(right) 初始值 a.length - 1 每次递减
for (int right = a.length - 1; right > 0; right--) {
int max = right;
for (int i = 0; i < right; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[max]) {
max = i;
}
}
swap(a, max, right);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
堆排序

要点
- 建立大顶堆
- 每次将堆顶元素(最大值)交换到末尾,调整堆顶元素,让它重新符合大顶堆特性
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {
9, 5, 7, 12, 1, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void heapSort(int[] a) {
heapify(a, a.length);
for (int right = a.length - 1; right > 0; right--) {
swap(a, 0, right);
down(a, 0, right);
}
}
// 建堆 O(n)
private static void heapify(int[] a, int size) {
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
down(a, i, size);
}
}
// 下潜
// 非递归比递归的实现快大约6ms
private static void down(int[] a, int parent, int size) {
while (true) {
int left = parent * 2 + 1;
int right = left + 1;
int max = parent;
if (left < size && a[left] > a[max]) {
max = left;
}
if (right < size && a[right] > a[max]) {
max = right;
}
if (max == parent) {
// 没找到更大的孩子
break;
}
// 找到了更大的孩子
swap(a, max, parent);
parent = max;
}
}
// 交换
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
插入排序
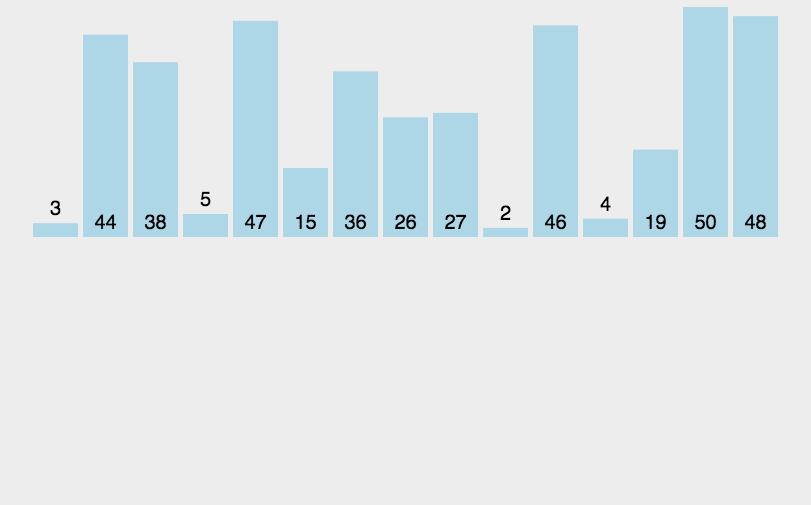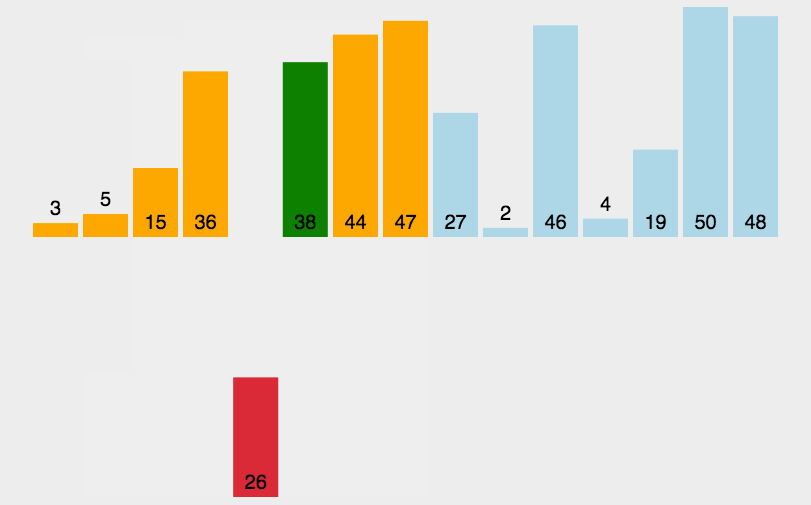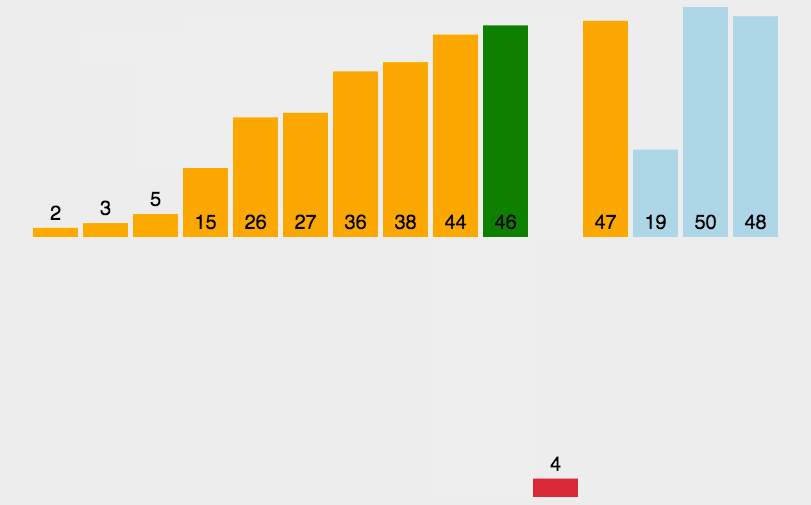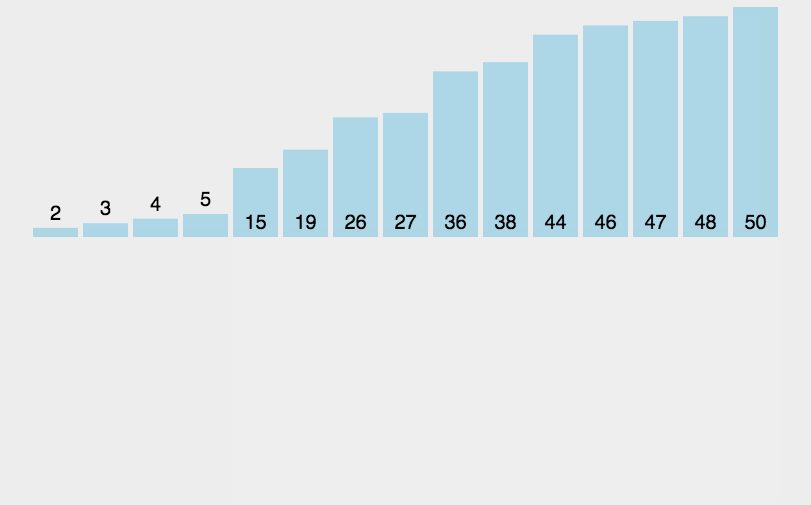
要点
- 将数组分为两个部分[0…low][low…a.length-1]
- 左边[0…low]是已排序部分
- 右边[low…a.length-1]是未排序部分
- 每次从未排序区域取出low位置的元素,插入已排序区域
public class InsertionSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {
9, 5, 7, 12, 1, 3};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
insertion(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
private static void insertion(int[] a) {
for (int low = 1; low < a.length; low++) {
int temp = a[low];
int i = low - 1;
// 自右向左找插入位置,如果比待插入元素大,则不断右移,空出插入位置
while (i >= 0 && temp < a[i]) {
a[i + 1] = a[i];
i--;
}
// 找到插入位置
if (i != low - 1) {









