目录
- [剑指 Offer II 006. 排序数组中两个数字之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kLl5u1/)——简单
- [剑指 Offer II 007. 数组中和为 0 的三个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/1fGaJU/)——中等
- [剑指 Offer II 014. 字符串中的变位词](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/MPnaiL/)——中等
- [剑指 Offer II 018. 有效的回文](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/XltzEq/)——简单
- [剑指 Offer II 019. 最多删除一个字符得到回文](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/RQku0D/)——简单
- [剑指 Offer II 021. 删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/SLwz0R/)——中等
- [剑指 Offer II 022. 链表中环的入口节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/c32eOV/)——中等
- [剑指 Offer II 023. 两个链表的第一个重合节点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3u1WK4/)——简单
- [剑指 Offer II 026. 重排链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/LGjMqU/)——中等
- [剑指 Offer II 027. 回文链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/aMhZSa/)——简单
- [剑指 Offer II 056. 二叉搜索树中两个节点之和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/opLdQZ/)——简单
- [剑指 Offer II 077. 链表排序](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/7WHec2/)——中等

剑指 Offer II 006. 排序数组中两个数字之和——简单
题目描述:

题解
方法一:数组已经排序了,直接首尾双指针;
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int arr[] = new int[2];
int i = 0;
int j = numbers.length-1;
while(i<=j) {
if (numbers[i]+numbers[j]>target) {
j--;
}else if (numbers[i]+numbers[j]<target) {
i++;
}else {
arr[0]=i;
arr[1]=j;
break;
}
}
return arr;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 007. 数组中和为 0 的三个数——中等
题目描述

题解:
方法一:暴力破解(超时)
题解链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/1fGaJU/solution/jian-dan-yi-dong-javac-pythonjs-san-shu-nu6el/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
if (nums==null||nums.length<3) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
Set<List<Integer>> res = new HashSet<>();
Arrays.sort(nums); // 时间复杂度 O(nlogn)
// Set<List<Integer>> set = new HashSet<>();
// O(n^3)
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) {
for (int k = j+1; k < nums.length; k++) {
if (nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]==0) {
// List<Integer> temp = Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]);
// Collections.sort(temp); // 对list排序
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]));
}
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(res);
}
}
方法二:双指针
题解链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/1fGaJU/solution/jian-dan-yi-dong-javac-pythonjs-san-shu-nu6el/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums){
if (nums==null||nums.length<3) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<List<Integer>> res= new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums); // 时间复杂度 O(nlogn)
//时间复杂度 O(n^2)
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-2; i++) { // 时间复杂度O(n)
// i 去重
if (i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1]) {
continue;
}
// 在 i + 1 ... nums.length - 1 中查找相加等于 -nums[i] 的两个数
int target = -nums[i];
int left = i+1;
int right = nums.length-1;
while (left<right) { // 时间复杂度O(n)
int sum = nums[left]+nums[right];
if (sum==target) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]));
// 去重 如果前一个left==后面的left 跳过
// while (left<right&& nums[left]==nums[++left]);
// while (left<right&& nums[right]==nums[--right]);
while (left<right) {
left++;
if (nums[left-1]!=nums[left]) {
break; // 当left-1 !=left 的时候 跳出left++循环 左指针去重完毕
}
}
while (left<right) {
right--;
if (nums[right]!=nums[right+1]) {
break; // 当 right != right+1的时候 跳出right--循环 右指针去重完毕
}
}
}else if (sum < target) {
left++;
}else {
right--;
}
}
}
return res; // O(n)
}
}
剑指 Offer II 014. 字符串中的变位词——中等
题目描述

题解
class Solution {
public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
int m = s1.length();
int n = s2.length();
if (m>n) {
return false;
}
int cnt1[] = new int[26];
for (char c:s1.toCharArray()) {
cnt1[c - 'a']++;
}
int left = 0;
int cnt2[] = new int[26];
for(int right =0;right < n;right++) {
int idx = s2.charAt(right) - 'a';
cnt2[idx]++;
while (cnt2[idx]>cnt1[idx]) {
cnt2[s2.charAt(left)-'a']--;
left++;
}
if (right-left+1==m) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
优化
class Solution {
public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
int n = s1.length();
int m = s2.length();
int cnt[] = new int[26];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
cnt[s1.charAt(i)-'a']--;
}
int left = 0;
for(int right=0;right<m;right++) {
int in = s2.charAt(right)-'a';
cnt[in]++;
while(cnt[in]>0) {
cnt[s2.charAt(left)-'a']--;
left++;
}
if (right-left+1==n) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
复杂度分析

剑指 Offer II 018. 有效的回文——简单
题目描述

题解
方法一:无脑判断思维reverse()

class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
s = s.toLowerCase();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (Character.isLetterOrDigit(c)) {
sb.append(c);
}
}
return sb.toString().equals(new StringBuffer(sb).reverse().toString());
}
}
方法二:双指针

class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int left = 0;
int right = s.length() - 1;
s = s.toLowerCase();
char c1;
char c2;
while (left < right) {
if (!Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(left))) {
left += 1;
} else if (!Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(right))) {
right -=1;
} else {
c1 = s.charAt(left);
left++;
c2 = s.charAt(right);
right--;
if (c1 != c2) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 019. 最多删除一个字符得到回文——简单
题目描述:
题解

class Solution {
public boolean validPalindrome(String s) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int left = 0;
int right = s.length()-1;
while (left<right) {
// 如果不相等,则分两种情况:删除左边的元素,或者右边的元素,再判断各自是否回文,满足一种即可。
if (s.charAt(left)!=s.charAt(right)) {
return isPalindrome(s, left+1, right)||isPalindrome(s, left, right-1);
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
// 判断字符串 s 的 [left, right] 是否回文
public boolean isPalindrome(String s, int left,int right) {
while (left<right) {
if (s.charAt(left)!=s.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}
复杂度分析
剑指 Offer II 021. 删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点——中等
题目描述
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:

题解

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 创建辅助头节点,head , fast 和 slow 都指向这个辅助头节点
ListNode fast = new ListNode(0);
fast.next = head;
head = fast;
ListNode slow = fast;
// fast 指针先走 n + 1 个单位
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
// fast 指针和 slow 指针一起移动,直到 fast 指向空后,slow 指针则指向倒数第 n + 1个节点。
while (fast != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
// 删除倒数第 n 个节点
slow.next = slow.next.next;
// 由于我们设置了辅助头节点,所以 head.next 才是链表的首元节点。
return head.next;
}
}
复杂度分析
剑指 Offer II 022. 链表中环的入口节点——中等
题目描述

示例 1:
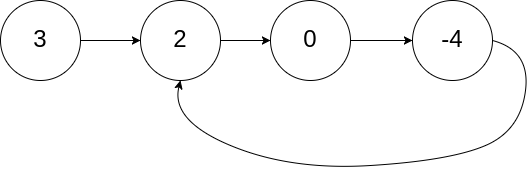

示例 2:
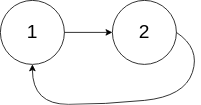

示例 3:



题解
方法一:哈希表
一个非常直观的思路是:我们遍历链表中的每个节点,并将它记录下来;一旦遇到了此前遍历过的节点,就可以判定链表中存在环。借助哈希表可以很方便地实现。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode pos = head;
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (pos !=null) {
if (set.contains(pos)) {
return pos;
} else {
set.add(pos);
}
pos = pos.next;
}
return pos;
}
}
复杂度分析


方法二:快慢指针
-
假设快慢指针相遇时,慢指针slow走了k步,那么快指针fast一定走了2k步
-

-
fast一定比slow多走了k步,这多走的k步其实就是fast指针在环里转圈圈,所以k的值就是环长度的「整数倍」
-
假设环的起点到相遇点的距离为m,见下图,环的起点距头结点head的距离为k - m,也就是说如果从head前进k - m步就能到达环起点。
-
如果从相遇点继续前进k - m步,也恰好到达环起点。因为结合上图的 fast 指针,从相遇点开始走k步可以转回到相遇点,那走k - m步肯定就走到环起点了
-

-
只要我们把快慢指针中的任一个重新指向head,然后两个指针同速前进,k - m步后一定会相遇,相遇之处就是环的起点了
-
寻找入环节点可查看快慢指针法:快慢指针相遇为入环点原理也讲清楚了,一看便知
-
想要了解单链表的各种技巧的单链表的六大解题套路,你都见过么?
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 快慢指针初始化指向 head
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
// 快指针走到末尾时停止
while (fast!=null) {
// 慢指针走一步,快指针走两步
slow = slow.next;
if (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;
}
// 快慢指针相遇,说明含有环
if (slow == fast) {
// 任一节点指向头节点
fast = head;
// 同步向前进
while (fast!=slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 返回入口节点
return fast;
}
}
// 不包含环
return null;
}
}
复杂度分析


剑指 Offer II 023. 两个链表的第一个重合节点——简单
题目描述


题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:


示例 2:


示例 3:



题解
方法一:双指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode n1 = headA;
ListNode n2 = headB;
int size1 = 0;
int size2 = 0;
// 获取A的长度
while (n1!=null) {
size1++;
n1 = n1.next;
}
// 获取B的长度
while (n2!=null) {
size2++;
n2 = n2.next;
}
// 将A,B中较长的一个移动dif步,使两个链表一样长
if (size1 > size2) {
int dif = size1 - size2;
for (int i = 0; i < dif; i++) {
headA = headA.next;
}
}else {
int dif = size2 - size1;
for (int i = 0; i < dif; i++) {
headB = headB.next;
}
}
// 遍历链表公共节点
while (headA!=null) {
if (headA==headB) {
return headA;
}else {
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}
复杂度分析

解法二:哈希集合

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode temp = headA;
while (temp!=null) {
set.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while (temp!=null) {
if (set.contains(temp)) {
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
复杂度分析


解法三:双指针(最优)


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA==null||headB==null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pa = headA;
ListNode pb = headB;
while (pa!=pb) {
if (pa==null) {
pa = headB;
}else{
pa = pa.next;
}
if (pb==null) {
pb = headA;
}else{
pb = pb.next;
}
}
return pa;
}
}
复杂度分析


剑指 Offer II 026. 重排链表——中等

示例 1:


示例 2:



题解
方法一:线性表
因为链表不支持下标访问,所以我们无法随机访问链表中任意位置的元素。
因此比较容易想到的一个方法是,我们利用线性表存储该链表,然后利用线性表可以下标访问的特点,直接按顺序访问指定元素,重建该链表即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null) {
return ;
}
List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<ListNode>();
ListNode node = head;
while (node!=null) {
list.add(node);
node = node.next;
}
int i = 0;
int j = list.size()-1;
while (i < j) {
list.get(i).next = list.get(j);
i++;
if (i == j) {
break;
}
list.get(j).next = list.get(i);
j--;
}
list.get(i).next = null;
}
}
复杂度分析


方法二:寻找链表中点 + 链表逆序 + 合并链表
注意到目标链表即为将原链表的左半端和反转后的右半端合并后的结果。
这样我们的任务即可划分为三步:
- 找到原链表的中点(参考「876. 链表的中间结点」)。
-
- 我们可以使用快慢指针来 O(N)O(N) 地找到链表的中间节点。
- 将原链表的右半端反转(参考「206. 反转链表」)。
-
- 我们可以使用迭代法实现链表的反转。
- 将原链表的两端合并。
-
- 因为两链表长度相差不超过 11,因此直接合并即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 寻找链表中点+链表逆序+合并链表
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null) {
return;
}
ListNode mid = middleNode(head);
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
l2 = reverseList(l2);
mergeList(l1, l2);
}
// 寻找链表中点
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 链表逆序
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return pre;
}
// 合并链表
public void mergeList(ListNode l1,ListNode l2) {
ListNode l1Temp;
ListNode l2Temp;
while (l1 != null && l2 !=null) {
l1Temp = l1.next;
l2Temp = l2.next;
l1.next = l2;
l1 = l1Temp;
l2.next = l1;
l2 = l2Temp;
}
}
}
复杂度分析


方法三:寻找链表中点 + 链表逆序 + 合并链表(清风python)
 清风
清风






class Solution {
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode();
ListNode slow = pre;
ListNode fast = pre;
pre.next = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode half = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode rev_half = this.reverseList(half);
ListNode cur = pre.next;
while (rev_half != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = rev_half;
cur = cur.next;
rev_half = rev_half.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
复杂度分析

剑指 Offer II 027. 回文链表——简单
题目描述
给定一个链表的 头节点 head **,**请判断其是否为回文链表。
如果一个链表是回文,那么链表节点序列从前往后看和从后往前看是相同的。
示例 1:


示例 2:



题解
方法一:将值复制到数组中后用双指针法


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr!=null) {
list.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.next;
}
int i = 0;
int j = list.size()-1;
while (i<j) {
if (!list.get(i).equals(list.get(j))) {
return false;
}
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
}
复杂度分析


方法二:stringbuffer版本 reserve
java sb版本 由于val是个位数 可以直接反转对比
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer reserve = new StringBuffer();
while (head!=null) {
sb.append(head.val);
reserve.append(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
reserve.reverse();
return sb.toString().equals(reserve.toString());
}
}
复杂度分析

剑指 Offer II 056. 二叉搜索树中两个节点之和——简单
题目描述
给定一个二叉搜索树的 根节点 root 和一个整数 k , 请判断该二叉搜索树中是否存在两个节点它们的值之和等于 k 。假设二叉搜索树中节点的值均唯一。
示例 1:

示例 2:


题解
方法一:递归加Map
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Map<Integer ,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
boolean flag = false;
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) {
if(root == null){
return flag;
}
int val = root.val;
if(map.containsKey(k-val)){
flag = true;
return flag;
}
map.put(val , k-val);
findTarget(root.right,k);
findTarget(root.left,k);
return flag;
}
}
复杂度分析

方法二:“哈希表”+“DFS”

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) {
// 创建一个哈希表:存放已经遍历过的节点值
Set<Integer> set= new HashSet<>();
// 辅助栈:辅助进行中序遍历
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 中序遍历
while (root!=null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(root!=null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
// 判断哈希表中是否存在 `k - val`
if(set.contains(k-node.val)) {
return true;
}
set.add(node.val);
root = node.right;
}
return false;
}
}

剑指 Offer II 077. 链表排序——中等
题目描述
给定链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:


示例 2:


示例 3:


题解
方法一:java 归并 (递归实现 )
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return head;
}
// 第一步:将链表拆分成两半
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode prev = head;
while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null) {
prev = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
prev.next = null;
// 第二步:将两部分的链表分别排序
ListNode l1 = sortList(head);
ListNode l2 = sortList(slow);
// 第三步:合并两个有序链表
return merge(l1, l2);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode l1,ListNode l2) {
ListNode p = new ListNode();
ListNode l = p;
while (l1 != null && l2 !=null) {
if (l1.val<l2.val) {
p.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else {
p.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if (l1!=null) {
p.next = l1;
}
if (l2!=null) {
p.next = l2;
}
return l.next;
}
}

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
// 思路归并排序
// 将 链表分成 两个长度相差 不超过 1 的链表
// 分别将 两个链表排序 后 再合并有序链表 ;
class Solution {
// 这个方法 可以是认为 用来排序 链表
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 给 链表排序 动用归并排序思想
// 把 链表分成两个差不多长度链表 分别排序后 合并
// 将链表 拆分成 多个部分多次合并
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
// 得到第一次分割
ListNode head1 = head;
ListNode head2 = split(head);
// 将两个链表分别排序
head1 = sortList(head1);
head2 = sortList(head2);
return merge(head1,head2);
}
// 将以 head 为头结点的链表分成两个差不多长度的链表
private ListNode split(ListNode head){
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}// 当 fast == null 时 slow 就是 下一个链表的头
ListNode ans = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
return ans;
}
// 合并 两个有序链表
private ListNode merge(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){
if(l1 == null) return l2;
if(l2 == null) return l1;
if(l1.val > l2.val){
l2.next = merge(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
l1.next = merge(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}
}
复杂度分析













