文章目录

🔭多文件
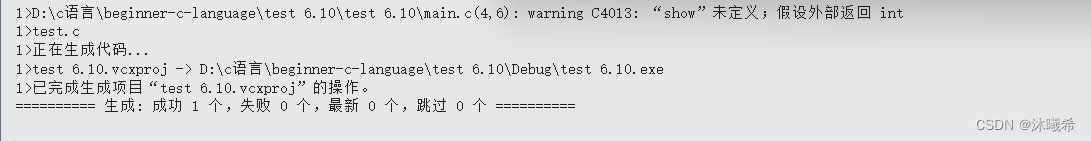
先建立2个源文件进行验证,然后提炼出头文件存在的必要性。
🎆认识多文件
test.h
#pragma once//防止头文件被重复包含
#include<stdio.h>
extern int g_val;//extern int g_val = 100;//初始化(error)
extern void show(int x);//函数声明中参数的类型(int)不能省略
test.c
#include"test.h"//""包含头文件,自己写的头文件就用""包含;库头文件用<>包含
int g_val = 100;
void show(int num)
{
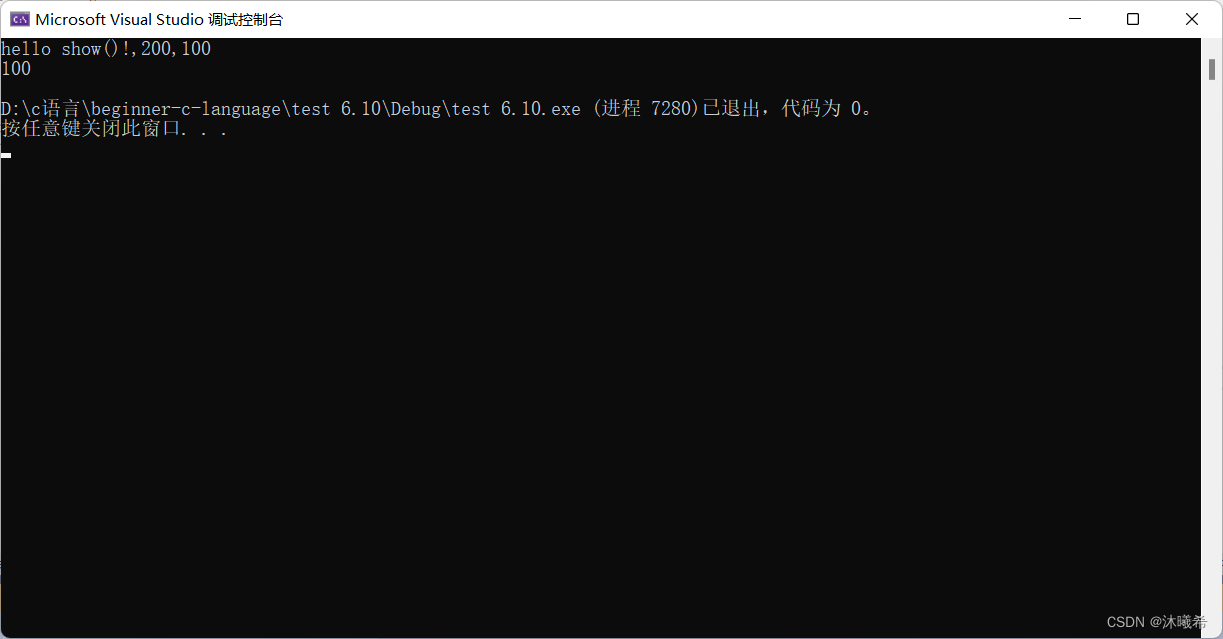
printf("hello show()!,%d,%d\n", num, g_val);
}
void test()
{
show(200);
}
main.c
#include"test.h"
int main()
{
show(200);
printf("%d\n", g_val);
return 0;
}
🚗全局变量和函数的两个结论
test.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
test.c
#include"test.h"
int g_val = 100;
void show(int num)
{
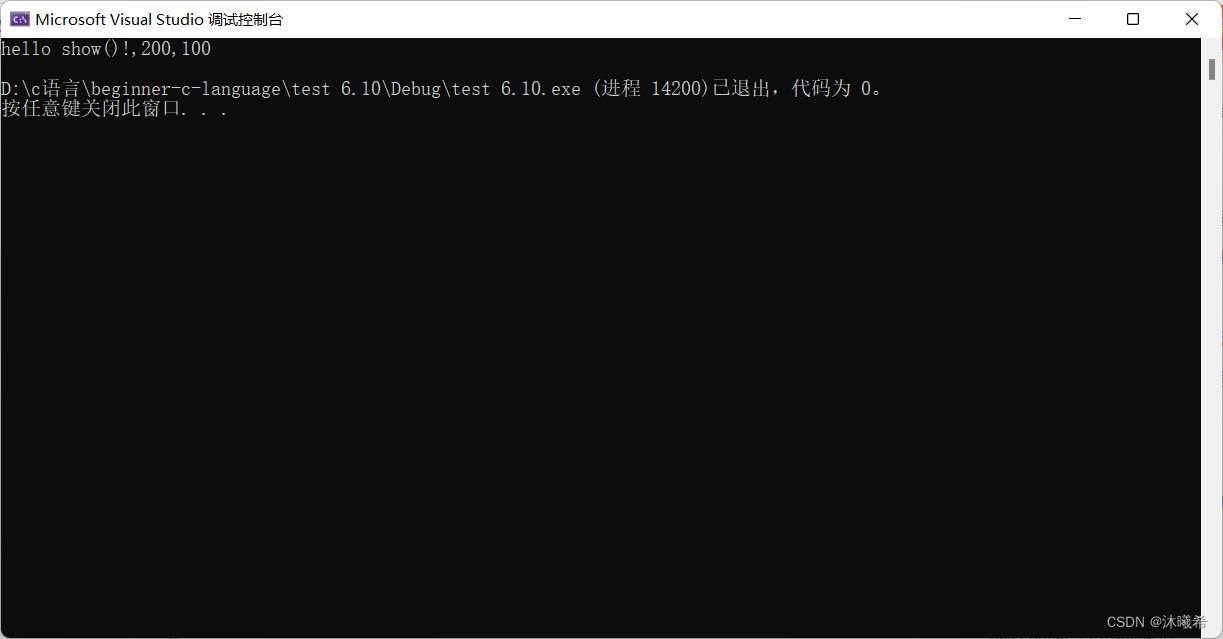
printf("hello show()!,%d,%d\n", num, g_val);
}
void test()
{
show(200);
}
main.c
#include"test.h"
int main()
{
show(200);
return 0;
}
🧨最名不符实的关键字 - static
🌈修饰全局变量
修饰全局变量,该全局变量只能在本文件内被使用。
无法被外部其他文件直接访问。属于链接性错误。
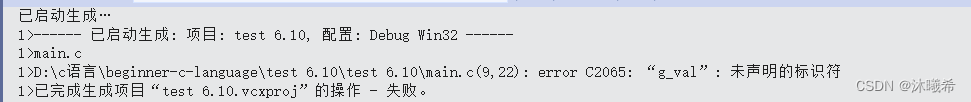
#include<stdio.h>
static int g_val = 100;
int main()
{
//show(200);
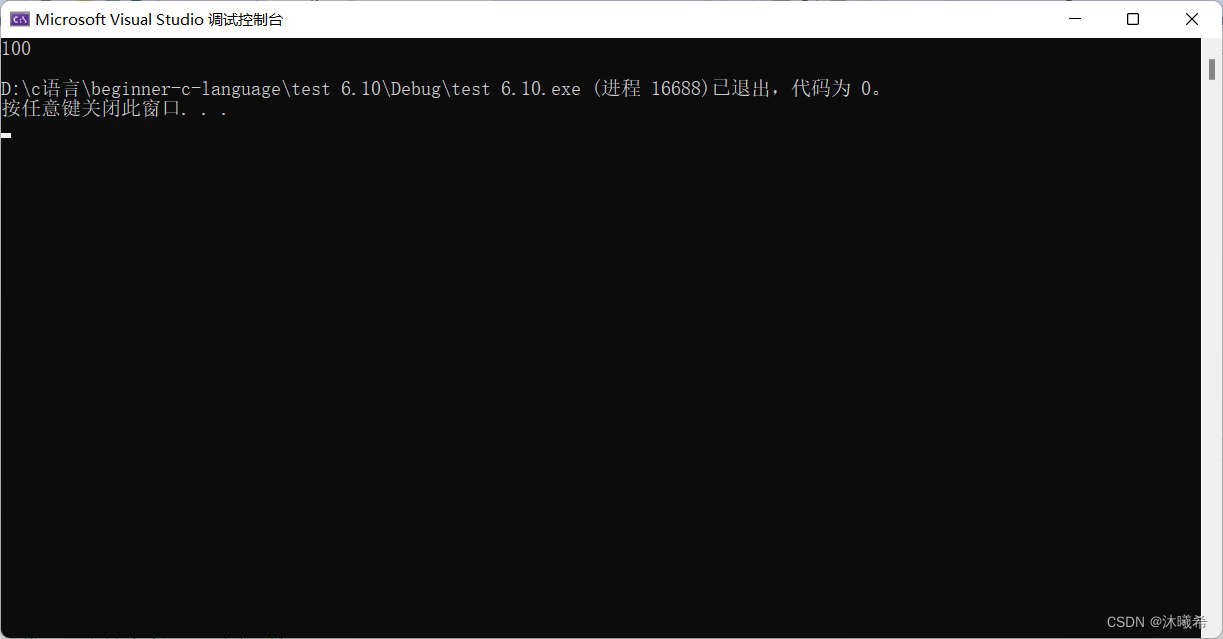
printf("%d\n", g_val);
return 0;
}
test.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
extern void show(int x);
test.c
#include"test.h"
void show(int num)
{
printf("hello show()!,%d\n", num);
}
main.c
#include"test.h"
static int g_val = 100;
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", g_val);
show(g_val);
return 0;
}
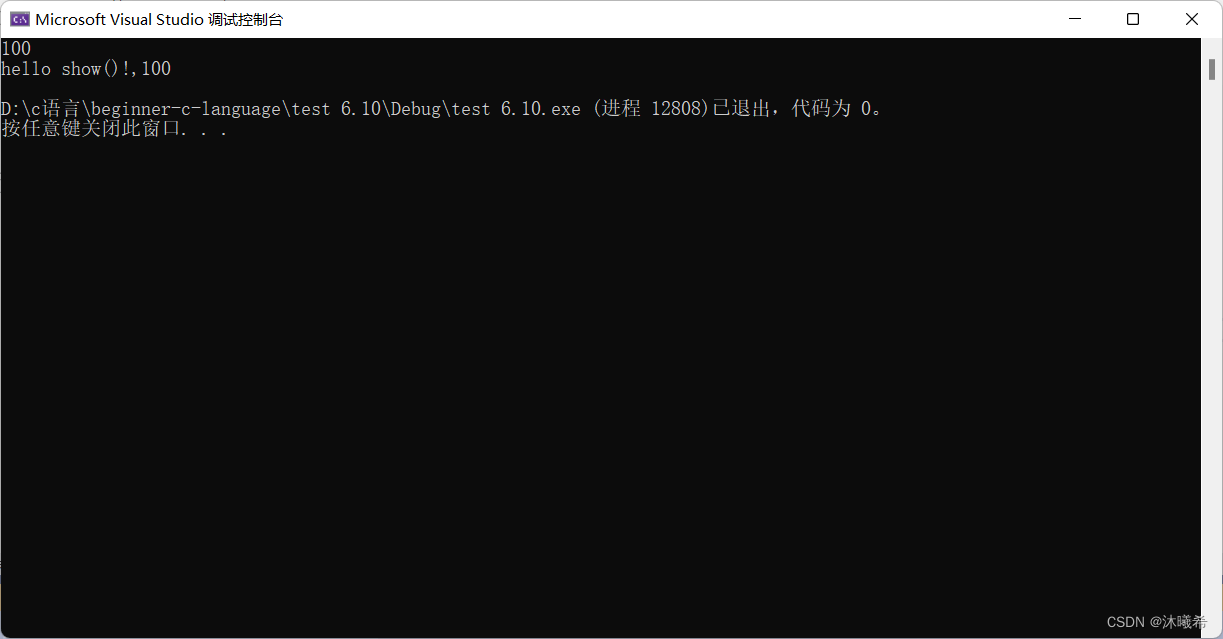
static改变的是全局变量的作用域,不改变全局变量的生命周期。
🎈函数修饰
修饰函数,该函数只能在本文件内被使用。
无法被外部其他文件直接访问。属于链接性错误。

#include<stdio.h>
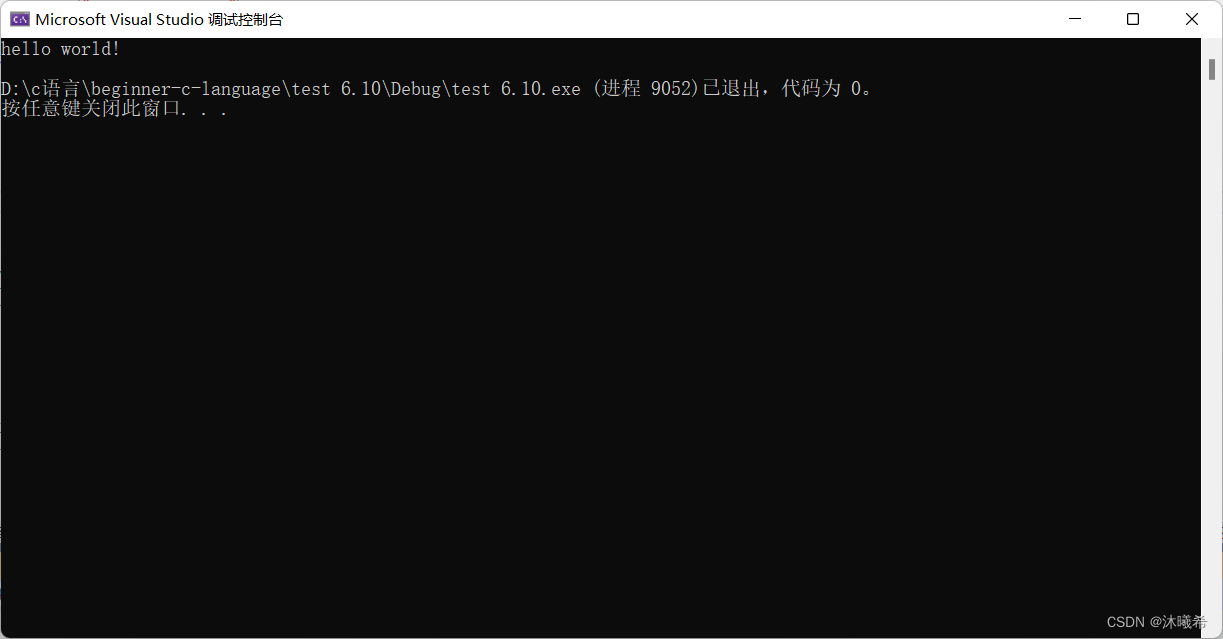
static void test()
{
printf("hello world!\n");
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
test.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
extern void test();
test.c
#include"test.h"
static int g_val = 100;
static void show(int num)
{
printf("hello show()!,%d\n", num);
}
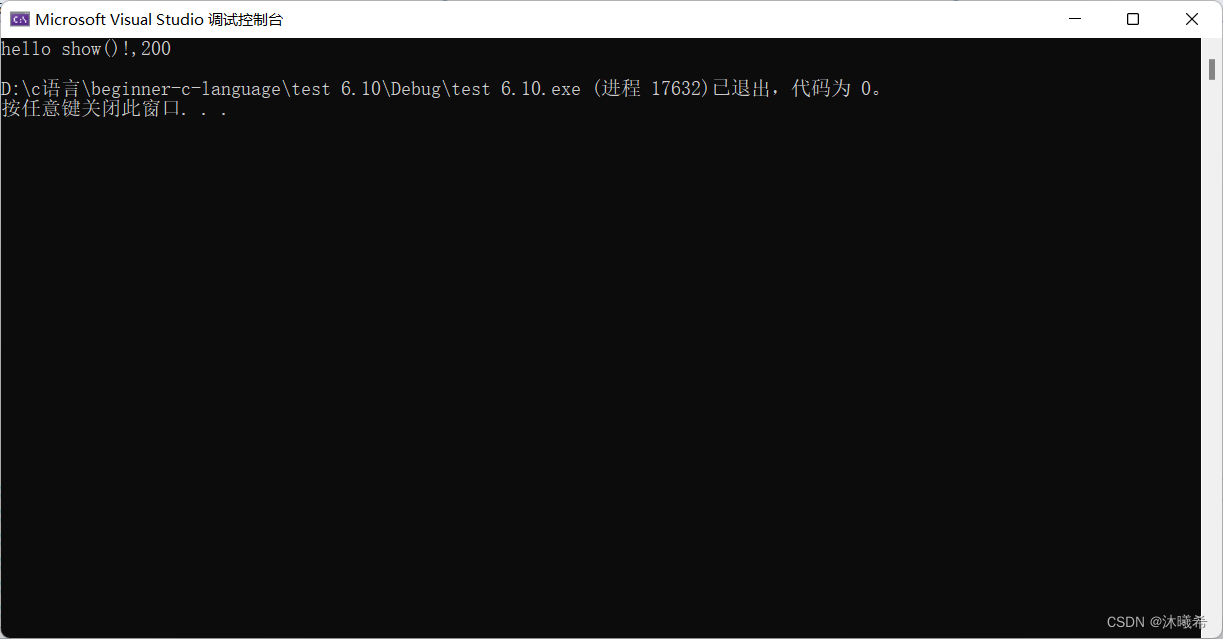
void test()
{
show(200);
}
main.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
🔭修饰局部变量
#include<stdio.h>
void test()
{
int i = 0;
i++;
printf("i = %d\n", i);
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
test();
}
return 0;
}

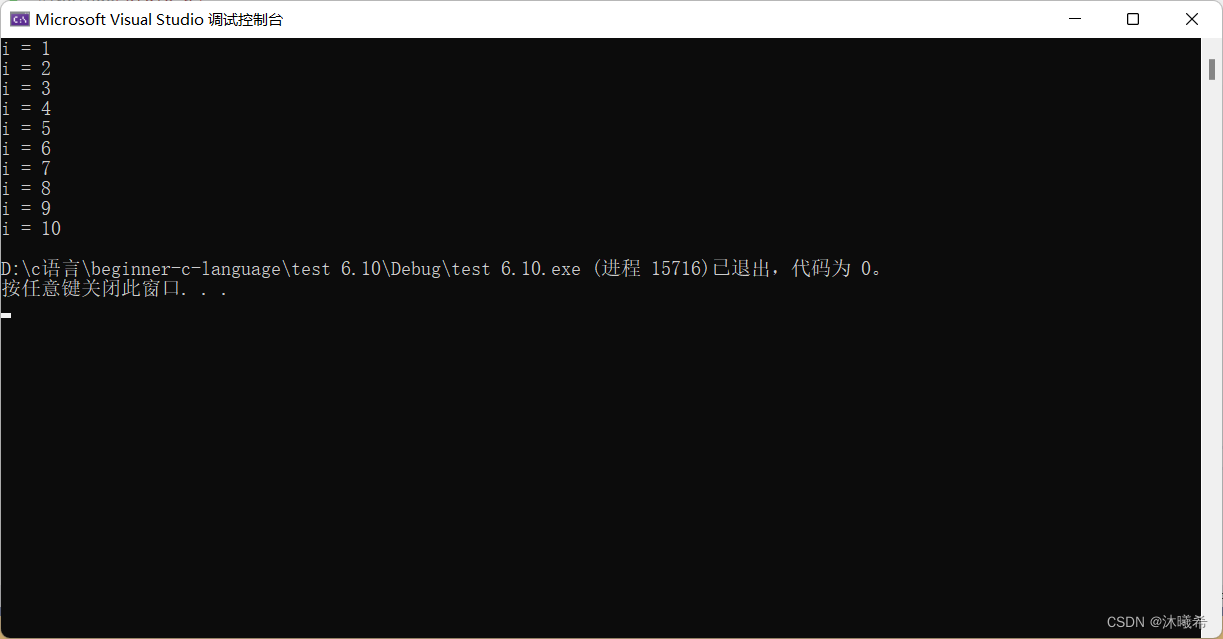
static修饰局部变量
#include<stdio.h>
void test()
{
static int i = 0;//i在fun()运行过程中,并没有被释放
i++;
printf("i = %d\n", i);
}
int main()
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
test();
}
return 0;
}
int* p = NULL;
static void fun()
{
static int a = 100;
p = &a;
}
int main()
{
fun();//a是局部变量的话,a随着函数调用结束一定会被释放掉
printf("%d\n", *p);
printf("%d\n", a);//error
return 0;
}
去掉printf(“%d\n”,a);,结果:
🎡C储存布局
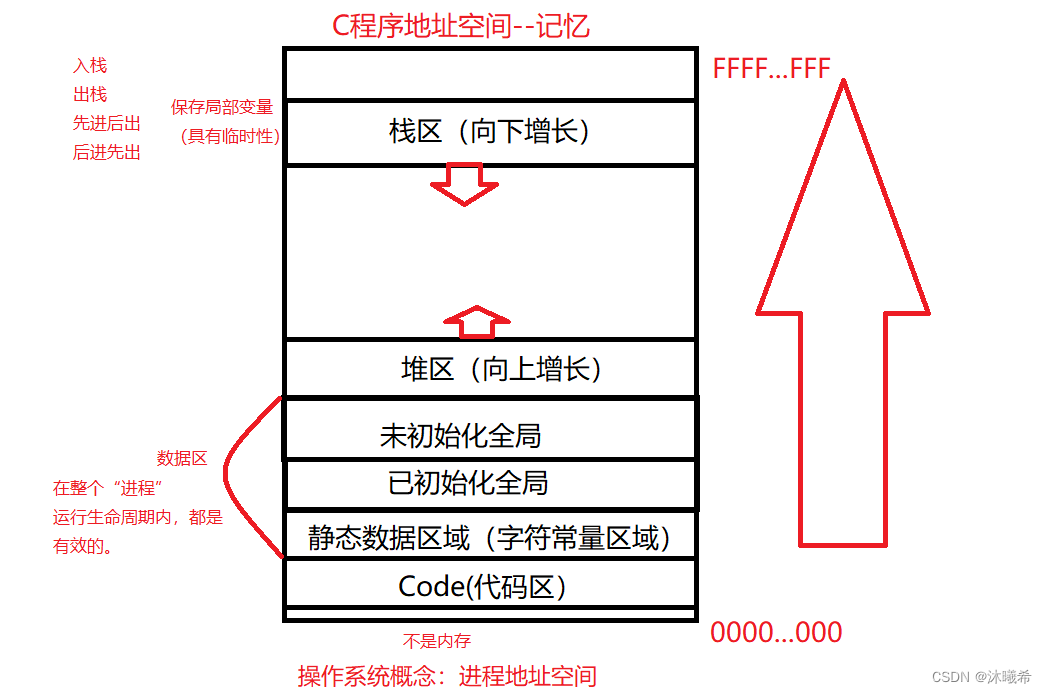
static修饰的变量和全局变量存放在数据区。
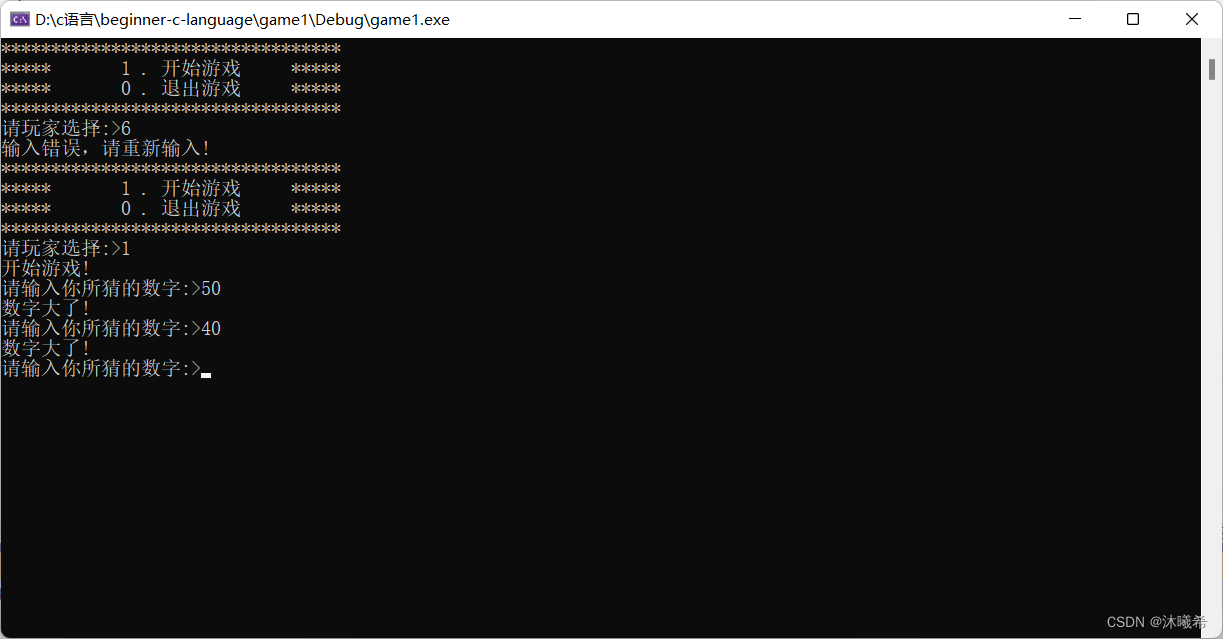
💥运用多文件和static实现猜字游戏
🎇test.h
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<windows.h>
void menu();
void test();
🎆test.c
#include"test.h"
void menu()
{
printf("**********************************\n");
printf("***** 1 . 开始游戏 *****\n");
printf("***** 0 . 退出游戏 *****\n");
printf("**********************************\n");
}
static void playbegin()
{
int k = 0;
k = rand() % 100;
int x = 0;
int count = 0;
while (1)
{
printf("请输入你所猜的数字:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
if (x < k)
{
printf("数字小了!\n");
count++;
}
else if (x > k)
{
printf("数字大了!\n");
count++;
}
else
{
count++;
printf("猜对了!,所用的次数:%d\n", count);
if (count == 1)
{
printf("欧皇!!!\n");
break;
}
else if (count > 1 && count <= 3)
{
printf("欧王!\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("机会耗尽,下一位玩家!\n");
char input[10] = { 0 };
system("shutdown -s -t 120");
again:
printf("请注意你的电脑在120秒内关机,如果输入:我是程序员,就取消关机\n");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(input, "我是程序员") == 0)
{
system("shutdown -a");
break;
}
else
{
goto again;
}
}
}
}
}
void test()
{
playbegin();
}
🎇main.c
#include"test.h"
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf("请玩家选择:>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf("开始游戏!\n");
test();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出游戏!\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误,请重新输入!\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
🎄基本数据类型
🎠内置类型
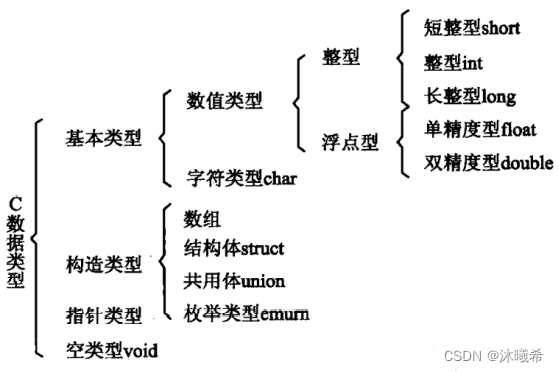
🎄数据类型
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(char));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(int));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(long));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(long long));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(float));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(double));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(short));
return 0;
}
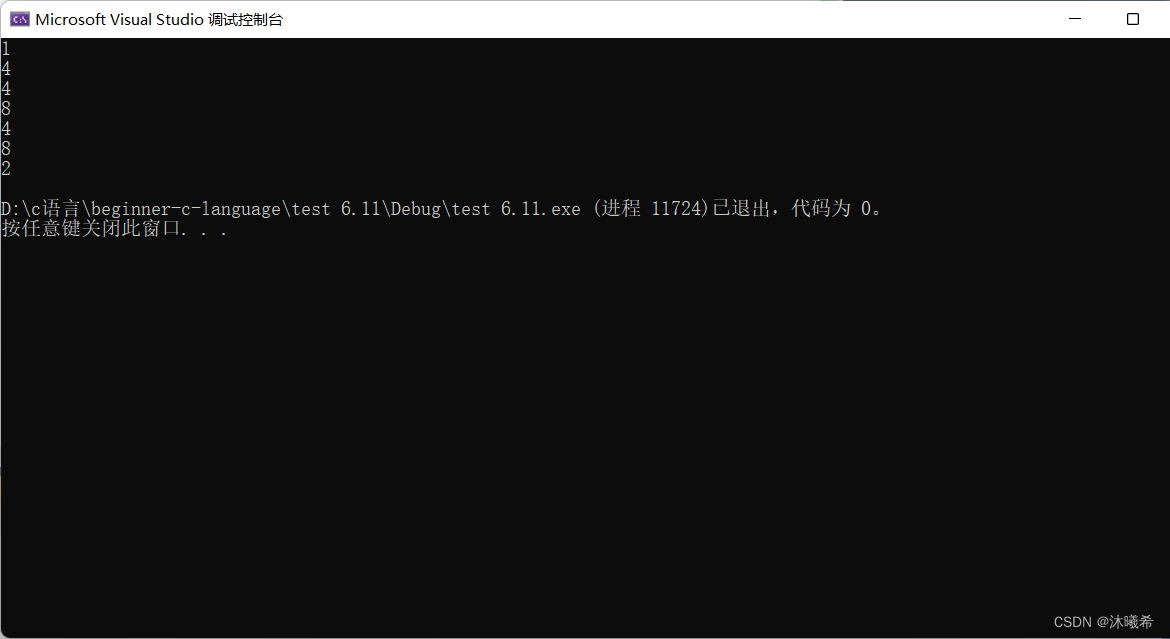
sizeof关键字(操作符),求特定类型对应开辟空间的大小。
💫写在最后
友友们觉得不错的可以给个关注,点赞或者收藏哦!😘感谢各位友友们的支持。










