530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
示例:

提示:树中至少有 2 个节点
解析:
数组求长度用length
字符串长度用length()
集合长度用size()
利用好二叉搜索树的特性,只需要中序遍历,就一定可以得到一个有序的数组,此时挨个遍历最小间距即可。
class Solution {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
traveral(root);
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 1; i < res.size(); i++){
result = Math.min(result,res.get(i) - res.get(i-1));
}
return result;
}
private void traveral(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
traveral(root.left);
res.add(root.val);
traveral(root.right);
}
}还有一种双指针法,算是新思路,设置pre为前一个节点,这样在中序遍历过程中就可以得出最小间距,省去用集合存储这一步了。
class Solution {
TreeNode pre; //记录前一个节点
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
traveral(root);
return result;
}
void traveral(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
traveral(root.left);
if(pre != null){
result = Math.min(result, root.val-pre.val);
}
pre = root;
traveral(root.right);
}
}501.二叉搜索树中的众数
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。
假定 BST 有如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含结点的值小于等于当前结点的值
- 结点右子树中所含结点的值大于等于当前结点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
例如:
给定 BST [1,null,2,2],

返回[2].
提示:如果众数超过1个,不需考虑输出顺序
进阶:你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
解析:
双指针的做法,定义一个pre为当前节点的前一个节点,考虑到二叉搜索树的特性,可以不断更新最大频率,以及出现最大频率的那个元素。这种不使用额外的空间,实时存储最大频率的元素。
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> res;
int maxCount; //记录最高的频率
int count; //记录频率
TreeNode pre; //前一个节点
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
maxCount = 0;
count = 0;
pre = null;
findMode1(root);
int[] result = new int[res.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++){
result[i] = res.get(i);
}
return result;
}
void findMode1(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
findMode1(root.left); //左
int rootValue = root.val;
if(pre == null || rootValue != pre.val){ //pre为null表示是第一个节点,后者则表示重新统计频率
count = 1;
}else{
count++;
}
if(count > maxCount){
res.clear();
res.add(rootValue);
maxCount = count;
}else if(count == maxCount){
res.add(rootValue);
}
pre = root;
findMode1(root.right);
}
}236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
力扣题目链接(opens new window)
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
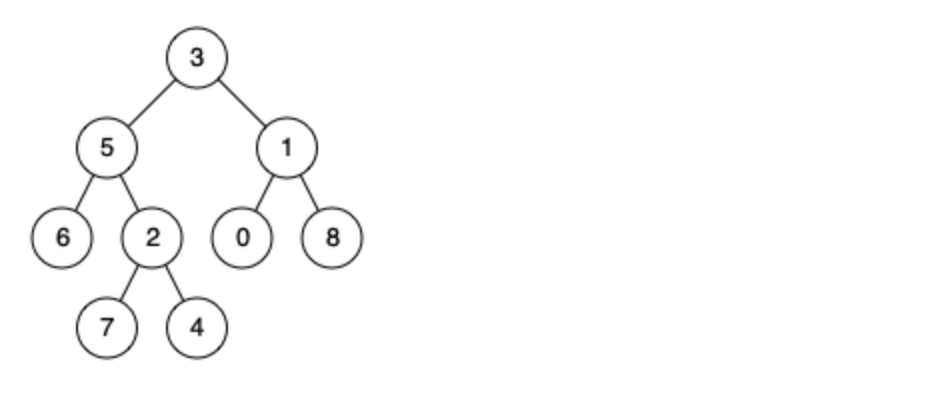
示例 1: 输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出: 3 解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
示例 2: 输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 输出: 5 解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
解析:
看到题目的想法是,如果p是q的子树或者q是p的子树,那么最近的公共祖先一定是其父节点;如果p和q在同一层上,那么就考虑根节点。大致思路是这些,选择看题解验证猜想。
卡哥的题解有点难理解,在力扣的题解区找了一家比较浅显易懂的解释:
我考虑的只是其中一种情况—>如果根节点是查找的p和q其一,或者根节点为空,则return root
还有情况二—>如果根节点不是查找的p和q,就往根节点的左右子树查找,那么如果左子树和右子树同时为null,说明p和q不存在于这个二叉树中,返回null;
情况三—>如果左右子树中有一个为空,即返回另一个子树。
情况四—>如果均不为空,则说明p和q分别存在于左右子树中,最近公共祖先节点是该root。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left == null && right == null){
return null;
}
if(left == null){
return right;
}
if(right == null){
return left ;
}
return root;
}
}









